在运营商/数据中心网络中,我们有时候会需要对服务器做出限速。传统的方法有对接口的限速或者对IP的限速,但是这种方法在某些情景下不太适用——比如说,如果只是想对某个方向做限速,比如欧洲方向,或者只对中国内地方向做限速,那么传统的接口或者IP限速就不太实用了。这里我们就需要用一些更弹性的方法来实现该需求。
这次的文章我们来讲解如何在 Juniper 以及 Cisco (IOS-XE) 路由器上实现该功能。
快速开始:什么是QPPB?
众所周知,QoS 策略在普通情景下是不能通过 AS-PATH 或者 BGP community 来进行操作的。而在复杂的运营商网络/数据中心网络中,针对目的 ASN /源 ASN 的 QoS 则是刚需。但是使用 ACL 来进行操作很不现实,大量的 ACL 会消耗路由器等网络设备的 TCAM,这种情况下我们就需要引入 QPPB 技术来实现该需求。
QPPB(QOS Policy Propagation Through the Border Gateway Protocol)技术是一项通过 BGP 路由策略部署 QOS 的技术,通过基于 BGP 路由的 community-list, AS paths list 和 ACL, Prefix-list 等属性进行路由分类,对不同的分类应用不同的QOS策略。
也就是说,我们可以通过该技术实现基于目标/源 ASN 的 QoS,包括限速/排队等功能,本文章着重介绍其中的限速功能。
拓扑图和需求信息如下:
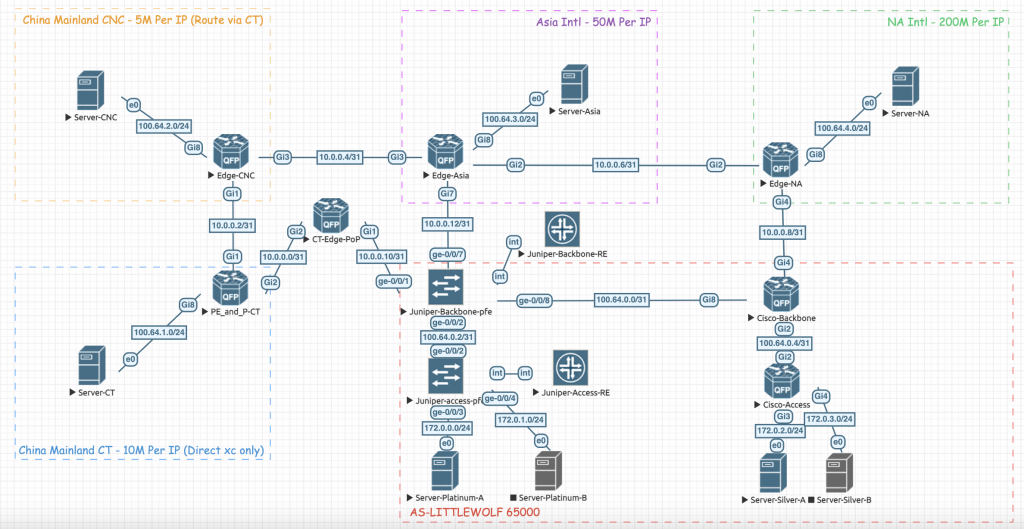
AS-LITTLEWOLF 决定对去往不同方向的流量进行限速,需求分别如下:
- 去往 CNC 的流量,限速至 5Mbps
- 去往 CT 的流量,限速至 10Mbps
- 去往 Asia – Intl 的流量,限速至 50Mbps
- 去往 NA – Intl 的流量,限速至 200Mbps
前期准备:QPPB 是怎么工作的?
普通的限速的步骤大致为以下几步:
- 对感兴趣的 Dest/Src IP地址或接口进行匹配
- 使用 Class-map 调用该 ACL (或者略过 1 阶段,直接默认全部匹配)
- 使用 Policy-map 调用 Class-map,并定义限速动作 ( Shaping or CIR )
- 接口调用 Policy-map,实现限速
但是在 QPPB 下,步骤则分为了这些:
- 对感兴趣的 BGP 路由进行抓取,写入 route-map 对感兴趣的路由进行预定义
- 使用 Table-map 对感兴趣的路由压入 QoS 标记 ( qos-group, ip precedence )
- 使用 Class-map 对 QoS 标记进行调用
- 使用 Policy-map 调用 Class-map,并定义限速动作 ( Shaping or CIR )
- 对感兴趣的流方向接口启动 BGP-policy,以启动 QPPB 功能(否则 Policy-map 不会生效)
- 接口调用 Policy-map,实现限速
Cisco 平台该功能名称为 QPPB,Juniper 平台则叫 SCU/DCU,实现都是同样的功能,只是配置略微有点不同。Juniper 平台我会在稍微后面再讲。
开始实验:配置 Cisco 的 QPPB 功能
我们决定使用 community 来实现标记功能,所以需要定义从每条链路收到的 Community (该部分配置已经省略),链路定义如下:
- 从 CT 收到的路由 – 100:1
- 从 Asia 收到的路由 – 100:2
- 从 NA 收到的路由 – 100:3
- 通过 CT 收到的 CNC 路由 – 9929:0
所有 community 均为标准 community。
ip community-list standard na permit 100:3 ip community-list standard asia permit 100:2 ip community-list standard ct permit 100:1 ip community-list standard cnc permit 9929:0 // 预先定义 community list (路由内的 community 为上游发过来已携带的值) route-map qppb permit 100 ordering-seq 100 match community na set ip qos-group 1 ! route-map qppb permit 110 ordering-seq 110 match community asia set ip qos-group 2 ! route-map qppb permit 115 ordering-seq 115 match community cnc set ip qos-group 4 ! route-map qppb permit 120 ordering-seq 120 match community ct set ip qos-group 3 ! route-map qppb permit 9999 ordering-seq 9999 ! named-ordering-route-map enable
使用 Routemap 做好分组后,进入 BGP 进程使用 Table-map 压入 QoS Group
router bgp 65000 table-map qppb // 调用写好的 route-map,对感兴趣的路由压入 QoS Group,做好标记
做好路由的 QoS 标记后,开始写 Class-map 以及 Policy-map,定义限速动作
class-map match-all na match qos-group 1 // 匹配预定义好的组( BGP 中的 Table-map 规则里面定义好的组) class-map match-all ct match qos-group 3 class-map match-all asia match qos-group 2 class-map match-all cnc match qos-group 4 ! policy-map traffic-shaping class na shape average 200000000 // 调用 class-map,对指定方向进行限速 class asia shape average 50000000 class ct shape average 10000000 class cnc shape average 5000000
到这里,规则就已经定义好了,调用的逻辑如下:
对感兴趣的路由压入 QoS Group 标记(这里使用 community 来进行匹配) –> Class-map 调用 QoS Group –> Policy-map 调用 Class-map 并规定限速动作 –> 接口激活 BGP-policy 后,调用 policy-map 进行限速
由于 traffic-shaping 是出站概念(排队概念),与 Policer CIR 概念不同,所以需要在出接口上调用。
interface GigabitEthernet2 (Upstream) ip address 100.64.0.5 255.255.255.254 (...protocol config ignored) service-policy output traffic-shaping // 在这个接口上调用 shaping policy,实现限速功能 interface GigabitEthernet3 (Downstream) ip address 172.0.2.1 255.255.255.0 (...protocol config ignored) bgp-policy destination ip-qos-map // 为 BGP QPPB 激活接口功能,激活 Upstream 的 shaping policy // 激活的是基于目的地址的匹配,匹配流量去往的目的地。如果是 Policy CIR 则是在该接口 inbound 方向调用 Policy-map
如果只是限制出网流量,则以上配置已经足够。但是如果要限制入站流量,则需要以下配置:
interface GigabitEthernet2 (Upstream) ip address 100.64.0.5 255.255.255.254 (...protocol config ignored) bgp-policy source ip-qos-map // 为 BGP QPPB 激活接口功能,激活 Downstream 的 shaping policy // 激活的是基于源地址的匹配,匹配流量的来源。如果是 Policy CIR 则是在该接口 inbound 方向调用 Policy-map interface GigabitEthernet3 (Downstream) ip address 172.0.2.1 255.255.255.0 (...protocol config ignored) service-policy output traffic-shaping // 在这个接口上调用 shaping policy,实现限速功能
配置完成,我们在下接 Cisco 路由器的服务器上来测试一下上下行:
root@localhost:~# iperf3 -c 100.64.1.2 -p 443 -t 5 // 去往 CT 的流量 Connecting to host 100.64.1.2, port 443 [ 5] local 172.0.2.2 port 15888 connected to 100.64.1.2 port 443 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr Cwnd [ 5] 0.00-1.00 sec 1.26 MBytes 10.5 Mbits/sec 42 33.9 KBytes [ 5] 1.00-2.00 sec 1.13 MBytes 9.49 Mbits/sec 0 28.3 KBytes [ 5] 2.00-3.00 sec 1.13 MBytes 9.46 Mbits/sec 0 25.5 KBytes [ 5] 3.00-4.00 sec 1.13 MBytes 9.46 Mbits/sec 0 28.3 KBytes [ 5] 4.00-5.00 sec 1.13 MBytes 9.50 Mbits/sec 0 28.3 KBytes - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr [ 5] 0.00-5.00 sec 5.78 MBytes 9.69 Mbits/sec 42 sender [ 5] 0.00-5.06 sec 5.73 MBytes 9.51 Mbits/sec receiver iperf Done. root@localhost:~# iperf3 -c 100.64.1.2 -p 443 -t 5 -R // 来自于 CT 的流量 Connecting to host 100.64.1.2, port 443 Reverse mode, remote host 100.64.1.2 is sending [ 5] local 172.0.2.2 port 15892 connected to 100.64.1.2 port 443 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate [ 5] 0.00-1.00 sec 1.24 MBytes 10.4 Mbits/sec [ 5] 1.00-2.00 sec 1.14 MBytes 9.57 Mbits/sec [ 5] 2.00-3.00 sec 1.14 MBytes 9.57 Mbits/sec [ 5] 3.00-4.00 sec 1.14 MBytes 9.57 Mbits/sec [ 5] 4.00-5.00 sec 1.14 MBytes 9.56 Mbits/sec - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr [ 5] 0.00-5.04 sec 5.86 MBytes 9.76 Mbits/sec 443 sender [ 5] 0.00-5.00 sec 5.80 MBytes 9.74 Mbits/sec receiver
root@localhost:~# iperf3 -c 100.64.2.2 -p 443 -t 5 // 去往 CNC 的流量 Connecting to host 100.64.2.2, port 443 [ 5] local 172.0.2.2 port 22762 connected to 100.64.2.2 port 443 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr Cwnd [ 5] 0.00-1.00 sec 739 KBytes 6.05 Mbits/sec 26 67.9 KBytes [ 5] 1.00-2.00 sec 498 KBytes 4.08 Mbits/sec 0 22.6 KBytes [ 5] 2.00-3.00 sec 581 KBytes 4.76 Mbits/sec 0 22.6 KBytes [ 5] 3.00-4.00 sec 602 KBytes 4.94 Mbits/sec 0 28.3 KBytes [ 5] 4.00-5.00 sec 580 KBytes 4.75 Mbits/sec 0 22.6 KBytes - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr [ 5] 0.00-5.00 sec 2.93 MBytes 4.92 Mbits/sec 26 sender [ 5] 0.00-5.08 sec 2.88 MBytes 4.76 Mbits/sec receiver iperf Done. root@localhost:~# iperf3 -c 100.64.2.2 -p 443 -t 5 -R // 来自于 CNC 的流量 Connecting to host 100.64.2.2, port 443 Reverse mode, remote host 100.64.2.2 is sending [ 5] local 172.0.2.2 port 22766 connected to 100.64.2.2 port 443 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate [ 5] 0.00-1.00 sec 636 KBytes 5.21 Mbits/sec [ 5] 1.00-2.00 sec 584 KBytes 4.78 Mbits/sec [ 5] 2.00-3.00 sec 584 KBytes 4.79 Mbits/sec [ 5] 3.00-4.00 sec 584 KBytes 4.78 Mbits/sec [ 5] 4.00-5.00 sec 583 KBytes 4.77 Mbits/sec - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr [ 5] 0.00-5.04 sec 2.95 MBytes 4.92 Mbits/sec 0 sender [ 5] 0.00-5.00 sec 2.90 MBytes 4.87 Mbits/sec receiver
root@localhost:~# iperf3 -c 100.64.3.2 -p 443 -t 5 // 去往 Asia 的流量 Connecting to host 100.64.3.2, port 443 [ 5] local 172.0.2.2 port 46002 connected to 100.64.3.2 port 443 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr Cwnd [ 5] 0.00-1.00 sec 6.06 MBytes 50.8 Mbits/sec 2212 110 KBytes [ 5] 1.00-2.00 sec 5.65 MBytes 47.4 Mbits/sec 0 73.5 KBytes [ 5] 2.00-3.00 sec 5.64 MBytes 47.3 Mbits/sec 0 70.7 KBytes [ 5] 3.00-4.00 sec 5.66 MBytes 47.5 Mbits/sec 0 73.5 KBytes [ 5] 4.00-5.00 sec 5.67 MBytes 47.5 Mbits/sec 0 65.0 KBytes - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr [ 5] 0.00-5.00 sec 28.7 MBytes 48.1 Mbits/sec 2212 sender [ 5] 0.00-5.07 sec 28.6 MBytes 47.4 Mbits/sec receiver iperf Done. root@localhost:~# iperf3 -c 100.64.3.2 -p 443 -t 5 -R // 来自于 Asia 的流量 Connecting to host 100.64.3.2, port 443 Reverse mode, remote host 100.64.3.2 is sending [ 5] local 172.0.2.2 port 46006 connected to 100.64.3.2 port 443 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate [ 5] 0.00-1.00 sec 6.03 MBytes 50.6 Mbits/sec [ 5] 1.00-2.00 sec 5.70 MBytes 47.8 Mbits/sec [ 5] 2.00-3.00 sec 5.70 MBytes 47.8 Mbits/sec [ 5] 3.00-4.00 sec 5.70 MBytes 47.8 Mbits/sec [ 5] 4.00-5.00 sec 5.70 MBytes 47.8 Mbits/sec - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr [ 5] 0.00-5.04 sec 28.9 MBytes 48.1 Mbits/sec 835 sender [ 5] 0.00-5.00 sec 28.8 MBytes 48.4 Mbits/sec receiver
root@localhost:~# iperf3 -c 100.64.4.2 -p 443 -t 5 // 去往 NA 的流量 Connecting to host 100.64.4.2, port 443 [ 5] local 172.0.2.2 port 18818 connected to 100.64.4.2 port 443 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr Cwnd [ 5] 0.00-1.00 sec 24.3 MBytes 204 Mbits/sec 1233 407 KBytes [ 5] 1.00-2.00 sec 22.9 MBytes 192 Mbits/sec 71 450 KBytes [ 5] 2.00-3.00 sec 22.5 MBytes 189 Mbits/sec 192 229 KBytes [ 5] 3.00-4.00 sec 22.9 MBytes 192 Mbits/sec 0 283 KBytes [ 5] 4.00-5.00 sec 22.8 MBytes 191 Mbits/sec 0 272 KBytes - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr [ 5] 0.00-5.00 sec 115 MBytes 193 Mbits/sec 1496 sender [ 5] 0.00-5.04 sec 115 MBytes 192 Mbits/sec receiver iperf Done. root@localhost:~# iperf3 -c 100.64.4.2 -p 443 -t 5 -R // 来自于 NA 的流量 Connecting to host 100.64.4.2, port 443 Reverse mode, remote host 100.64.4.2 is sending [ 5] local 172.0.2.2 port 18822 connected to 100.64.4.2 port 443 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate [ 5] 0.00-1.00 sec 23.9 MBytes 201 Mbits/sec [ 5] 1.00-2.00 sec 22.8 MBytes 191 Mbits/sec [ 5] 2.00-3.00 sec 22.8 MBytes 191 Mbits/sec [ 5] 3.00-4.00 sec 22.8 MBytes 191 Mbits/sec [ 5] 4.00-5.00 sec 22.8 MBytes 191 Mbits/sec - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr [ 5] 0.00-5.04 sec 116 MBytes 193 Mbits/sec 19 sender [ 5] 0.00-5.00 sec 115 MBytes 193 Mbits/sec receiver
这样 Cisco (IOS-XE) 就搞定了,符合需求。接下来我们来配置 Juniper 平台。
扩展学习:Juniper 平台使用 SCU/DCU 针对 ASN 进行限速
Juniper 的配置相对来说要易于理解,且调用逻辑比 Cisco IOS-XE 要清晰。接下来就是详细配置:
root@access> show policy-options...
community import-cnc-via-ct members [ 100:1 9929:0 ];
community import-from-asia members 100:2;
community import-from-ct members 100:1;
community import-from-na members 100:3;
// 预先定义 community list ( 路由内的 community 为上游发过来已携带的值 )
root@access> show policy-options policy-statement export-dcu-scu | no-more
term cnc {
from community import-cnc-via-ct;
then {
destination-class cnc-dcu; // 将该路由定义 Destination Class,用于匹配去往该区域的流量
source-class cnc-scu; // 将该路由定义 Source Class,用于匹配来自于该区域的流量
next policy; // 匹配上后,跳到下一个 policy ( 该处省略,lab 中为负载均衡 policy )
}
}
term ct {
from community import-from-ct;
then {
destination-class ct-dcu;
source-class ct-scu;
next policy;
}
}
term asia {
from community import-from-asia;
then {
destination-class asia-dcu;
source-class asia-scu;
next policy;
}
}
term na {
from community import-from-na;
then {
destination-class na-dcu;
source-class na-scu;
next policy;
}
}
term last {
then next policy;
}
root@access> show configuration routing-options forwarding-table
export [ export-dcu-scu lb-export ];
// 对转发表应用规则,压入 Source Class + Destination Class,为之后限速做准备
定义好 SC/DC 后,我们来编写限速规则。
root@access> show firewall policer...
policer cnc-via-ct {
if-exceeding {
bandwidth-limit 5m;
burst-size-limit 1m;
}
then discard;
}
policer asia {
if-exceeding {
bandwidth-limit 50m;
burst-size-limit 1m;
}
then discard;
}
policer na {
if-exceeding {
bandwidth-limit 200m;
burst-size-limit 1m;
}
then discard;
}
policer ct {
if-exceeding {
bandwidth-limit 10m;
burst-size-limit 1m;
}
then discard;
}
定义好限速 Policer 后,我们编写防火墙规则来调用 Policer ( Junos是使用防火墙规则调用的,和 Cisco 不一样 )
root@access> show firewall family inet filter scu-dcu-shaping | no-more
term dest:na {
from {
destination-class na-dcu; // 匹配去往 NA 的流量
source-address {
172.0.0.0/24;
}
}
then policer na; // 调用限速 Policer
}
term dest:asia {
from {
destination-class asia-dcu;
source-address {
172.0.0.0/24;
}
}
then policer asia;
}
term dest:ct {
from {
destination-class ct-dcu;
source-address {
172.0.0.0/24;
}
}
then policer ct;
}
term dest:cnc {
from {
destination-class cnc-dcu;
source-address {
172.0.0.0/24;
}
}
then policer cnc-via-ct;
}
term src:cnc {
from {
source-class cnc-scu; // 匹配来自于 CNC 的流量
}
then policer cnc-via-ct; // 调用 Policer
}
term src:ct {
from {
source-class ct-scu;
}
then policer ct;
}
term src:asia {
from {
source-class asia-scu;
}
then policer asia;
}
term src:na {
from {
source-class na-scu;
}
then policer na;
}
term last {
then accept;
}
root@access> show configuration forwarding-options
family inet {
filter {
output scu-dcu-shaping;
}
}
// 将该防火墙规则应用到全局的 forarding-option 上面。
// Juniper 也支持将策略应用于接口,但是 SCP/DCP 必须应用于 Output 方向,Input 方向会不起作用。
// Lab 模拟环境内应用于接口有 bug,所以这里决定应用于 forwarding-options,实机中两种方式均可以。
配置完毕了,我们在下接 Juniper 路由器的服务器上测试效果:
root@localhost:~# iperf3 -c 100.64.1.2 -p 443 -t 5 // 去往 CT 的流量 Connecting to host 100.64.1.2, port 443 [ 5] local 172.0.0.2 port 14538 connected to 100.64.1.2 port 443 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr Cwnd [ 5] 0.00-1.00 sec 1.79 MBytes 15.0 Mbits/sec 708 50.9 KBytes [ 5] 1.00-2.00 sec 1.22 MBytes 10.2 Mbits/sec 202 17.0 KBytes [ 5] 2.00-3.00 sec 1.19 MBytes 9.99 Mbits/sec 157 33.9 KBytes [ 5] 3.00-4.00 sec 1.16 MBytes 9.77 Mbits/sec 47 14.1 KBytes [ 5] 4.00-5.00 sec 1.12 MBytes 9.37 Mbits/sec 86 25.5 KBytes - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr [ 5] 0.00-5.00 sec 6.48 MBytes 10.9 Mbits/sec 1200 sender [ 5] 0.00-5.04 sec 6.42 MBytes 10.7 Mbits/sec receiver iperf Done. root@localhost:~# iperf3 -c 100.64.1.2 -p 443 -t 5 -R // 来自于 CT 的流量 Connecting to host 100.64.1.2, port 443 Reverse mode, remote host 100.64.1.2 is sending [ 5] local 172.0.0.2 port 14542 connected to 100.64.1.2 port 443 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate [ 5] 0.00-1.00 sec 1.73 MBytes 14.5 Mbits/sec [ 5] 1.00-2.00 sec 1.28 MBytes 10.7 Mbits/sec [ 5] 2.00-3.00 sec 1.15 MBytes 9.65 Mbits/sec [ 5] 3.00-4.00 sec 1.16 MBytes 9.73 Mbits/sec [ 5] 4.00-5.00 sec 1.13 MBytes 9.44 Mbits/sec - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr [ 5] 0.00-5.04 sec 6.53 MBytes 10.9 Mbits/sec 1148 sender [ 5] 0.00-5.00 sec 6.45 MBytes 10.8 Mbits/sec receiver
root@localhost:~# iperf3 -c 100.64.2.2 -p 443 -t 5 // 去往 CNC 的流量 Connecting to host 100.64.2.2, port 443 [ 5] local 172.0.0.2 port 18480 connected to 100.64.2.2 port 443 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr Cwnd [ 5] 0.00-1.00 sec 1.10 MBytes 9.23 Mbits/sec 510 11.3 KBytes [ 5] 1.00-2.00 sec 421 KBytes 3.45 Mbits/sec 250 56.6 KBytes [ 5] 2.00-3.00 sec 619 KBytes 5.07 Mbits/sec 47 22.6 KBytes [ 5] 3.00-4.00 sec 577 KBytes 4.73 Mbits/sec 46 22.6 KBytes [ 5] 4.00-5.00 sec 568 KBytes 4.66 Mbits/sec 69 25.5 KBytes - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr [ 5] 0.00-5.00 sec 3.24 MBytes 5.43 Mbits/sec 922 sender [ 5] 0.00-5.05 sec 3.21 MBytes 5.33 Mbits/sec receiver iperf Done. root@localhost:~# iperf3 -c 100.64.2.2 -p 443 -t 5 -R // 来自于 CNC 的流量 Connecting to host 100.64.2.2, port 443 Reverse mode, remote host 100.64.2.2 is sending [ 5] local 172.0.0.2 port 18484 connected to 100.64.2.2 port 443 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate [ 5] 0.00-1.00 sec 834 KBytes 6.83 Mbits/sec [ 5] 1.00-2.00 sec 699 KBytes 5.72 Mbits/sec [ 5] 2.00-3.00 sec 467 KBytes 3.82 Mbits/sec [ 5] 3.00-4.00 sec 718 KBytes 5.89 Mbits/sec [ 5] 4.00-5.00 sec 595 KBytes 4.88 Mbits/sec - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr [ 5] 0.00-5.04 sec 3.31 MBytes 5.52 Mbits/sec 966 sender [ 5] 0.00-5.00 sec 3.24 MBytes 5.43 Mbits/sec receiver
root@localhost:~# iperf3 -c 100.64.3.2 -p 443 -t 5 // 去往 Asia 的流量 Connecting to host 100.64.3.2, port 443 [ 5] local 172.0.0.2 port 58888 connected to 100.64.3.2 port 443 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr Cwnd [ 5] 0.00-1.00 sec 6.48 MBytes 54.3 Mbits/sec 1969 481 KBytes [ 5] 1.00-2.00 sec 5.55 MBytes 46.6 Mbits/sec 2273 997 KBytes [ 5] 2.00-3.00 sec 5.21 MBytes 43.7 Mbits/sec 2681 417 KBytes [ 5] 3.00-4.00 sec 4.80 MBytes 40.2 Mbits/sec 2244 625 KBytes [ 5] 4.00-5.00 sec 4.58 MBytes 38.4 Mbits/sec 1464 533 KBytes - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr [ 5] 0.00-5.00 sec 26.6 MBytes 44.6 Mbits/sec 10631 sender [ 5] 0.00-5.04 sec 25.9 MBytes 43.1 Mbits/sec receiver iperf Done. root@localhost:~# iperf3 -c 100.64.3.2 -p 443 -t 5 -R // 来自于 Asia 的流量 Connecting to host 100.64.3.2, port 443 Reverse mode, remote host 100.64.3.2 is sending [ 5] local 172.0.0.2 port 58892 connected to 100.64.3.2 port 443 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate [ 5] 0.00-1.00 sec 4.99 MBytes 41.8 Mbits/sec [ 5] 1.00-2.00 sec 5.78 MBytes 48.5 Mbits/sec [ 5] 2.00-3.00 sec 5.03 MBytes 42.2 Mbits/sec [ 5] 3.00-4.00 sec 5.33 MBytes 44.7 Mbits/sec [ 5] 4.00-5.00 sec 4.43 MBytes 37.2 Mbits/sec - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr [ 5] 0.00-5.04 sec 26.5 MBytes 44.2 Mbits/sec 10458 sender [ 5] 0.00-5.00 sec 25.6 MBytes 42.9 Mbits/sec receiver
root@localhost:~# iperf3 -c 100.64.4.2 -p 443 -t 5 -b 400M // 去往 NA 的流量 Connecting to host 100.64.4.2, port 443 [ 5] local 172.0.0.2 port 50024 connected to 100.64.4.2 port 443 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr Cwnd [ 5] 0.00-1.00 sec 19.8 MBytes 166 Mbits/sec 3853 452 KBytes [ 5] 1.00-2.00 sec 18.9 MBytes 159 Mbits/sec 3799 314 KBytes [ 5] 2.00-3.00 sec 22.9 MBytes 192 Mbits/sec 1522 123 KBytes [ 5] 3.00-4.00 sec 23.2 MBytes 194 Mbits/sec 1132 478 KBytes [ 5] 4.00-5.00 sec 23.3 MBytes 195 Mbits/sec 2893 574 KBytes - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr [ 5] 0.00-5.00 sec 108 MBytes 181 Mbits/sec 13199 sender [ 5] 0.00-5.03 sec 107 MBytes 179 Mbits/sec receiver iperf Done. root@localhost:~# iperf3 -c 100.64.4.2 -p 443 -t 5 -b 400M -R // 来自于 NA 的流量 Connecting to host 100.64.4.2, port 443 Reverse mode, remote host 100.64.4.2 is sending [ 5] local 172.0.0.2 port 50028 connected to 100.64.4.2 port 443 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate [ 5] 0.00-1.00 sec 11.1 MBytes 93.1 Mbits/sec [ 5] 1.00-2.00 sec 23.0 MBytes 193 Mbits/sec [ 5] 2.00-3.00 sec 23.0 MBytes 193 Mbits/sec [ 5] 3.00-4.00 sec 23.1 MBytes 194 Mbits/sec [ 5] 4.00-5.00 sec 23.2 MBytes 195 Mbits/sec - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr [ 5] 0.00-5.04 sec 104 MBytes 173 Mbits/sec 14906 sender [ 5] 0.00-5.00 sec 103 MBytes 174 Mbits/sec receiver
实验完成目标,符合需求。
由于这里使用了 Policer CIR,并不是 Shaping,TCP Flow 会在尝试突破限制的时候被丢弃,所以 Retry 比较多。
可以根据具体生产环境需求来使用 Traffic Shaping.
参考资料:
[ Cisco ] ASR9000/XR: Implementing QOS policy propagation for BGP (QPPB)
[ Juniper ] Accounting Options, Source Class, and Destination Class
《[ BGP ] 使用QPPB来实现基于 Community 的 QoS》有2个想法
这个看起来是针对一个用户或者一个端口的限速,不过我印象中记得运营商是针对per IP 进行的,这个也能实现吗?
一般会使用定制设备来实现,或者其他定制方案